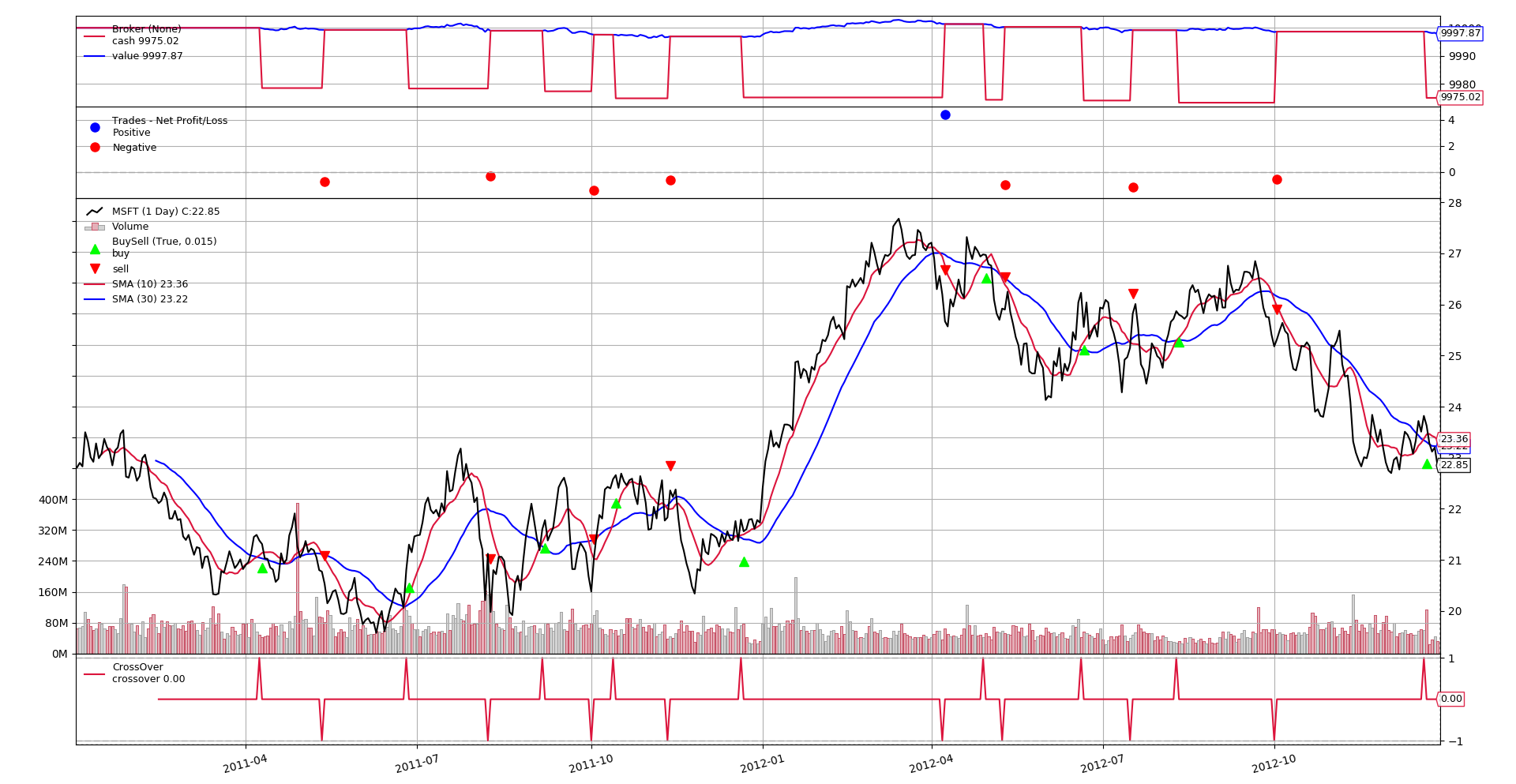
Hello Algotrading!
A classic Simple Moving Average Crossover strategy, can be easily implemented and in different ways. The results and the chart are the same for the three snippets presented below.
from datetime import datetime
import backtrader as bt
# Create a subclass of Strategy to define the indicators and logic
class SmaCross(bt.Strategy):
# list of parameters which are configurable for the strategy
params = dict(
pfast=10, # period for the fast moving average
pslow=30 # period for the slow moving average
)
def __init__(self):
sma1 = bt.ind.SMA(period=self.p.pfast) # fast moving average
sma2 = bt.ind.SMA(period=self.p.pslow) # slow moving average
self.crossover = bt.ind.CrossOver(sma1, sma2) # crossover signal
def next(self):
if not self.position: # not in the market
if self.crossover > 0: # if fast crosses slow to the upside
self.buy() # enter long
elif self.crossover < 0: # in the market & cross to the downside
self.close() # close long position
cerebro = bt.Cerebro() # create a "Cerebro" engine instance
# Create a data feed
data = bt.feeds.YahooFinanceData(dataname='MSFT',
fromdate=datetime(2011, 1, 1),
todate=datetime(2012, 12, 31))
cerebro.adddata(data) # Add the data feed
cerebro.addstrategy(SmaCross) # Add the trading strategy
cerebro.run() # run it all
cerebro.plot() # and plot it with a single command
from datetime import datetime
import backtrader as bt
# Create a subclass of Strategy to define the indicators and logic
class SmaCross(bt.Strategy):
# list of parameters which are configurable for the strategy
params = dict(
pfast=10, # period for the fast moving average
pslow=30 # period for the slow moving average
)
def __init__(self):
sma1 = bt.ind.SMA(period=self.p.pfast) # fast moving average
sma2 = bt.ind.SMA(period=self.p.pslow) # slow moving average
self.crossover = bt.ind.CrossOver(sma1, sma2) # crossover signal
def next(self):
if not self.position: # not in the market
if self.crossover > 0: # if fast crosses slow to the upside
self.order_target_size(target=1) # enter long
elif self.crossover < 0: # in the market & cross to the downside
self.order_target_size(target=0) # close long position
cerebro = bt.Cerebro() # create a "Cerebro" engine instance
# Create a data feed
data = bt.feeds.YahooFinanceData(dataname='MSFT',
fromdate=datetime(2011, 1, 1),
todate=datetime(2012, 12, 31))
cerebro.adddata(data) # Add the data feed
cerebro.addstrategy(SmaCross) # Add the trading strategy
cerebro.run() # run it all
cerebro.plot() # and plot it with a single command
from datetime import datetime
import backtrader as bt
# Create a subclass of SignaStrategy to define the indicators and signals
class SmaCross(bt.SignalStrategy):
# list of parameters which are configurable for the strategy
params = dict(
pfast=10, # period for the fast moving average
pslow=30 # period for the slow moving average
)
def __init__(self):
sma1 = bt.ind.SMA(period=self.p.pfast) # fast moving average
sma2 = bt.ind.SMA(period=self.p.pslow) # slow moving average
crossover = bt.ind.CrossOver(sma1, sma2) # crossover signal
self.signal_add(bt.SIGNAL_LONG, crossover) # use it as LONG signal
cerebro = bt.Cerebro() # create a "Cerebro" engine instance
# Create a data feed
data = bt.feeds.YahooFinanceData(dataname='MSFT',
fromdate=datetime(2011, 1, 1),
todate=datetime(2012, 12, 31))
cerebro.adddata(data) # Add the data feed
cerebro.addstrategy(SmaCross) # Add the trading strategy
cerebro.run() # run it all
cerebro.plot() # and plot it with a single command